Everything You Need to Know About IP Based Geolocation

Whether you are running an e-commerce store, trying to improve your website conversion rate, decrease bounce rates, or just make your website more friendly and memorable, IP-based geolocation may be the perfect solution for you. Nevertheless, IP-based geolocation has its pros and cons. It is important to recognize these advantages and disadvantages before incorporating it into your website.
In this article, we will explain how IP-based geolocation works, the types of information you can obtain, the accuracy of IP-based geolocation, how you can use IP-to-location service on your website, and more.
What is IP Based Geolocation?
Let’s start with some of the basics. IP-based geolocation is a way that you can find the location of an internet-connected computing or mobile device. To get started, all you need is your target’s IP address, which you can obtain using a simple PHP script, and a geolocation lookup tool.
A geolocation lookup tool canvasses public databases to determine the contact and registration information for a particular IP address. With both of these tools in hand, you simply input the IP address into the geolocation lookup tool and you will receive the location of your target.
What Is An IP Address?
An IP address is an online unique identifier for every computer or internet-connected phone. The standard IP address has four or six individual numbers that are separated by a decimal.
Through IP addresses, electronic devices can connect and share data with each other. Even though every computer or internet-connected device has its own IP address (“Local IP addresses”) these IPs are rarely accessible to the outside world.
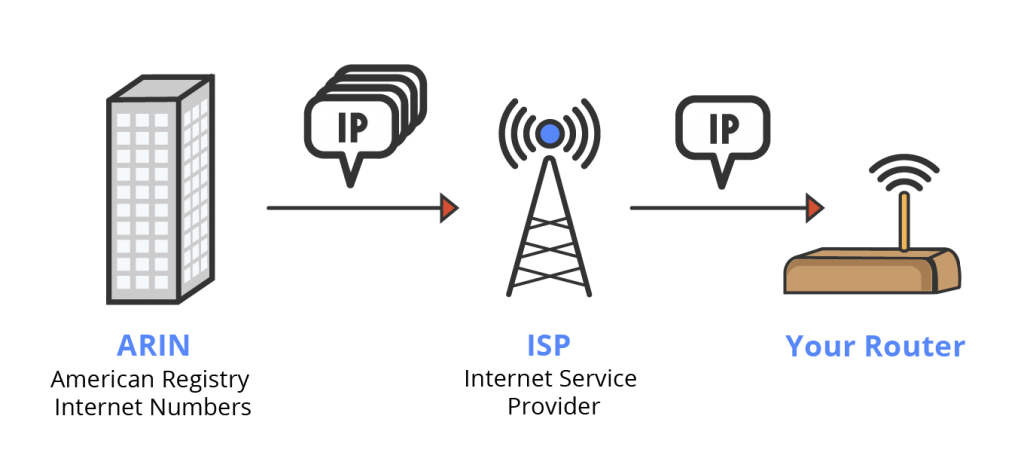
The heavy lifting is done through routers. Routers connect to individual computers, and then connect to the internet using their own IP address, also known as “External IP addresses.” The external IP address is provided by the user’s internet service provider, it is the one that actually being shared while browsing a website or otherwise acting on the internet.
The Geolocation Database
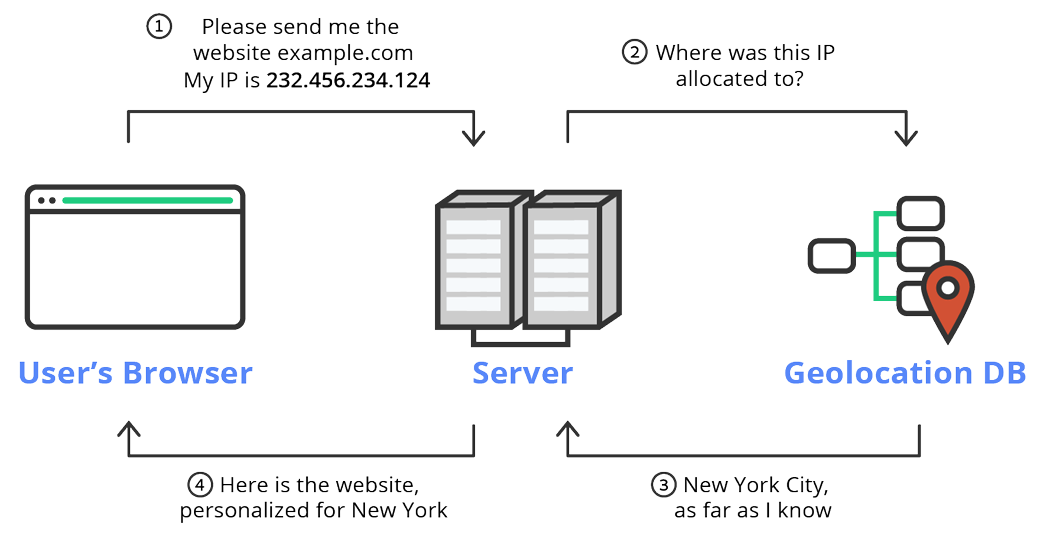
With an IP address, you can access a wide range of information. To reiterate, however, an IP address isn’t enough. You need to use a geolocation database to obtain this user information.
The most basic information provided in most geolocation databases includes the continent, country, state/region, city, and time zone of the electronic device. But along with this, you can discover the internet service provider (“ISP”), approximate longitude and latitude, and sometimes even the relevant organization attached to the device.
Common use cases for IP Based Geolocation
There are many different types of use cases for those who want to consider IP-based geolocation to locate online visitors. Here are a few common examples:
- Showing different offers to users from different locations: IP based geolocation can be used to emphasize a different product to users. For example, users in one location can obtain a physical product (like a course) while other users from a more distant location can be offered a book or online course.
- Show relevant business opening hours: IP based geolocation can show accurate business hours for a user who is in a particular country or state.
- Providing a localized feeling: IP based geolocation can display the name of a relevant state or country in a website title in order to provide a localized feeling and attract attention.
- Translating key messages to the user’s language: A complete translation of a site may be time-consuming, expensive and difficult to maintain. In many cases, using the user’s geolocation to translate key messages like titles and calls to action might do a great job reducing bounce rate and improving conversion rate. You can, for instance, translate key messages like titles and calls to action.
- Redirect visitors to a page in their language: You can leverage IP based geolocation to deliver content that is more targeted and relevant.
How an IP-to-Location Service Works
While it is critical to understand the value proposition of IP-based geolocation, it is also helpful to understand some of the more technical elements of IP-based geolocation. This isn’t compulsory, but it is nice to know.
As stated above, IP-based geolocation tools obtain the location of an electronic device through the IP address. With the IP address in hand, IP-based geolocation software pulls up data about the electronic device. It does this by canvassing a database to look for matches with the inputted IP address. Because these databases are created and maintained by third parties, the location data for electronic devices depends on the company that manages that data.
IP-to-Location Accuracy
IP-based geolocation services can only provide an approximate measure of geolocation accuracy. With these services, you can obtain 95 percent to 99 percent accuracy of a user’s country. IP-based geolocation services provide 55 percent to 80 percent accuracy for a user’s region or state. And they provide 50 percent to 75 percent accuracy for a user’s city.
In practice, the actual accuracy may vary from provider to provider and depending on the location of the device. For instance, IP-based geolocation services typically work better in big cities and work less well in smaller ones. Nevertheless, these IP-based geolocation services, in all likelihood, can provide enough accuracy to suit many needs.
Finally, there can be complications—especially if you are attempting to get the geolocation of a mobile device. Cell phones obtain new IP addresses as they move and cell phone providers service their users nationally. This means that it is more difficult to find an extremely precise location of a particular IP address.
Why isn’t IP-to-Location 100% accurate?
IP geolocation has been called “part art, part science” for several important reasons. First, there is no “ground truth” in IP-based geolocation that ties IP addresses to physical locations. ISPs (Internet Service Providers) assign dynamic IP addresses when users access the internet, and the precise accuracy of that location may depend on how they assign IP addresses to users.
Unvalidated registry data may lead to some inaccurate listings. Even things like inconsistent naming conventions can cause some inaccuracies—especially in cities. Challenges with latency measurements can make granular location data difficult in cities as well.
With all of these challenges in mind, however, IP-based geolocation can still deliver accurate location data. Yes, IP-based geolocation won’t deliver the most accurate location data every single time. It may not be able to provide a user’s location within one or two feet but it can still provide good enough accuracy for many needs.
Companies Providing Geolocation Databases
There are many IP geolocation database providers. While each database provider gets their IP address information from ARIN (or a different regional Internet Registry), the assignment regularly changes, as some database providers release unwanted IP addresses and others obtain new blocks of IP addresses. Along with this, there are different ways to get the data.
Some of the more popular IP geolocation database providers include IP2Location, IPligence, IP2C, DB-IP, and IP API. Most providers offer both free and paid plans, and two different ways to access the data – by downloading the database or by using an API.
Free vs Paid IP Geolocation Services
As mentioned, most geolocation database providers offer both free and paid plans. The main benefit of the free option is, quite obviously, its cost. That said, these services are usually less accurate than their paid counterparts. The free services may be appropriate if you are cost-conscious or if you are building a minimal viable product of your service. By contrast, the paid IP geolocation databases provide more accurate data and often provide dedicated support. Also, some of these paid IP geolocation databases can be quite expensive, so you will want to review potential costs before proceeding.
IP Geolocation Databases vs. Web API Services
Along with the free versus paid difference, IP geolocation database providers usually offer two different ways to access the data. You can either download the database itself or access it through an application programming interface.
Downloading the Database
The first option is downloading the database and hosting it on your server. By opting for downloading the IP geolocation database, you won’t face bandwidth restrictions as you would with an API database. You can submit as many requests as you want per day to your database, which can be especially helpful if your application requires many queries per day.
Nevertheless, there are some downsides to downloading the database. A downloaded IP geolocation database may not have as updated of a database as compared to an API database. This means that you may not have as accurate of data compared to accessing your data through an API. In addition, you may face some more technical challenges in downloading and setting up your database.
Accessing Data Through an API
One of the most significant benefits of accessing your data through an API is that the database is constantly updated. In addition, the onus is on the third-party provider to ensure that the data is available to your application. This allows you to focus on your product rather than on building and maintaining the database. There are some downsides, however. API databases may also contain some downtime, which may be inconvenient when you need the data. API databases, while they contain more updated information, may also limit the number of requests that you can make per day.
Choosing the Right Geolocation Plan
You will ultimately want to do your own due diligence, taking into account the advantages and disadvantages of each service. You will also want to account for the prices among the paid alternatives to see which service is most cost-effective for you. Each provider has different pricing methods and packages. Depending on your needs, one package may be more attractive than others. Think about what you need and which package will help you accomplish your objectives. Do not forget to consider your future needs. Applying the solution requires some technical work and you don’t want to waste time replacing providers as you grow.
Unless your site is a WordPress site and you choose to use a plugin that will do the technical work for you, whichever path you choose, you will need to have some knowledge of coding in order to implement a geolocation IP database. If you do not have this knowledge, you will need to rely on someone for help—whether that person is on your team or is a freelancer. While it may not be cost-prohibitive, this is another step that you will need to take in order to leverage a geolocation IP database for your website.
An alternative to detect the users’ location – the Geolocation API (HTML5)
Another way to access a user’s location is through a geolocation API. This is an HTML5 feature that lets a user share their location information with you. You have probably seen this feature when browsing the internet. You are shown an alert asking whether you want to share your location with a website. The decision is entirely at your discretion.
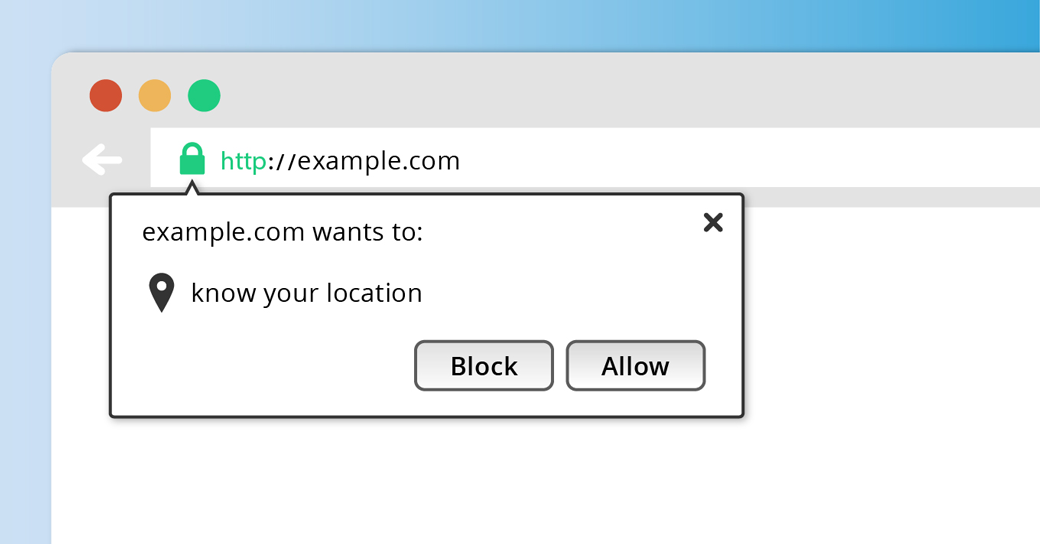
An advantage of the geolocation API is that it is automatically included in HTML5. However, there are some disadvantages. The main disadvantage is that you won’t be able to get a user’s location if they choose not to share it with you. This means that you won’t be able to access some of the key benefits of geolocation, like presenting personalized content to a user on his first visit. Along with this, the geolocation API only works on secure servers and it is not supported by certain browsers (like Internet Explorer 10 and below or OperaMini).
Using If-So WordPress Plugin to Display Website Content According to the User’s Location – No coding required
If-So Dynamic Content is a WordPress plugin that lets you leverage IP-based geolocation for your own website. The plugin does not require any coding—all you need to do is select the geolocation condition and set the content to display to users from targeted locations. You can try If-So’s geolocation completely for free. Setting it up takes less than 2 minutes.
Related Articles
- How to leverage an IP based geolocation content using a WordPress Plugin (no coding required)
- Step-by-step: Track dynamic content with Google Analytics
- Personalization examples – Using dynamic content to improve the conversion rate